INTRODUCTION
You can tell a field is maturing when the news stops feeling like a bag of party tricks and starts reading like operations. This week, robots did not simply dance, they clocked in. Chips moved from slides to capex. Standards arrived with certification, not promises. In short, the stack keeps compounding. Call it Robotics news September 13 2025 and you would not be wrong. The signal is not a single flashy demo. It is a steady drumbeat of systems that connect, learn, and ship.
I read these cycles with two lenses, engineering and economics. The first asks if the work clears the hard constraints, latency, dexterity, reliability, cost. The second asks if the incentives align. That is the thread that ties together humanoids, port logistics, campus fleets, and wearable assistive tech. Each slot is a productivity story. If you follow Robotics news today and the broader arc of Robotics News, consider this your map for Robotics news September 13 2025.
Table of Contents
1.MUSK UNVEILS TESLA AI ROBOTICS ROADMAP
Elon Musk used the All In Summit to make one claim: productivity solves debt when robots and intelligence scale. The centerpiece is Optimus Gen 3, a humanoid built for human level dexterity in the forearms and hands. Tesla stacks vertical control from custom AI chips to 26 actuator arms to cut cost and speed iteration. Musk says the car was hard, Starship harder, and Optimus sits between them. At volume the target is about twenty thousand dollars per unit.
If those hands deliver, labor heavy work changes shape. Factory kitting, back room retail, eldercare, and warehouse picking move from hopeful demos to scheduled work. The second pillar is silicon and software. AI5 promises large jumps in memory, bandwidth, and perceived driving skill, with FSD v14 framed as safer than human. Add Starlink direct to phone and cheaper Starship launches, and you get one bold integrated bet on throughput and reach.
2. SEMICON TAIWAN 2025 SIGNALS AI SUPERCYCLE
SEMICON Taiwan’s pre show sounded like a starting horn for an AI supercycle. Executives from SEMI, ASE, GlobalWafers, and NTU lined up on one point, AI workloads are spilling from cloud to edge, so fabs, advanced packaging, and standards must stretch together. The program spans more than two dozen forums across 13 tracks and 200 speakers, a sign that slide decks have turned into build lists.
Fresh forecasts add velocity.
Hyperscaler capex is expected to climb from 210 to 310 billion dollars in 2025, while AI and HPC gear could pass half of equipment spend by 2030. Taiwan plans a 28 billion dollar push led by GAA, HBM, chiplets, and 3D stacking. Alliances are keeping pace, from a 3DIC group to E187 cybersecurity certification. The talent pipeline is live, startups have a stage, and memory chiefs share a panel. That mix turns buzz into baselines for the next two years.
3. BERKELEY HUMANOID ROBOT RALLIES PAST 100 IN REAL PING PONG
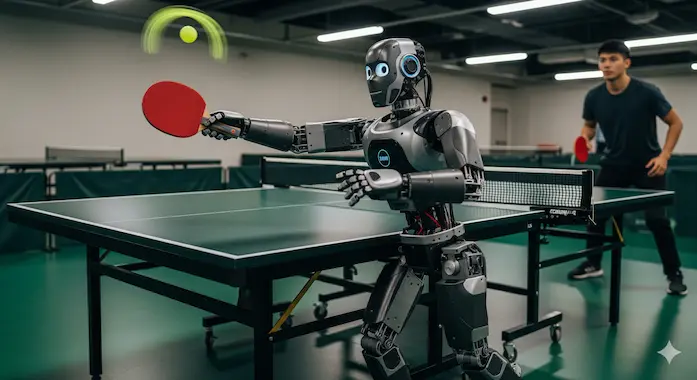
UC Berkeley’s HITTER hits back. The humanoid table tennis setup rallies past one hundred shots with a human, reading spin, stepping into returns, and stabilizing with its off arm like a weekend amateur. The stack splits jobs cleanly, external cameras estimate ball flight, a planner picks targets, and a reinforcement learner turns intent into coordinated whole body motion that lands on a regulation table.
The robot runs on a Unitree G1, which makes the story method over exotic hardware. The video matters because it crosses a threshold that ball machines and fixed arms never met, footwork plus perception plus timing, repeated. Table tennis compresses dexterous manipulation into a small court, and it is easy to score, rally length, spin, placement. If the team generalizes to lighting, styles, and heavier spin, HITTER becomes a blueprint for service robots that must react in homes, clinics, and factories at real speed with consistency.
4. SLIG NET CRACKS LOW LIGHT SPACE GRASPING
SLiG Net takes on a space robot’s worst day, dim images, free floating targets, and no table to lean on. The system couples LIFE Net, a low light enhancer that boosts structure without boosting noise, with HMPG Net, a grasp planner that fuses RGB and point cloud cues. The planner chooses grasps that balance contact stability, flatness, and center of mass alignment, a safer bet when microgravity removes helpful friction.
Results land in two buckets. Images recover detail with fewer parameters than heavyweight restorers, which fits tight thermal and power budgets. Grasping improves average precision on GraspNet 1 Billion and keeps success high even when scenes are barely lit. The contribution is less about novelty parts and more about coupling. Space work breaks pipelines that assume fixed frames and bright labs. SLiG Net truly moves orbital servicing and debris cleanup from slide deck to flight checklist.
5. SPECPRUNE VLA CUTS LATENCY WITHOUT KILLING SUCCESS
SpecPrune VLA trims what vision language action models do not need to think about, then trims again as depth grows, and finally trims less when motions get delicate. The approach reuses attention from the last step to keep globally important tokens, prunes background redundancy early, and recalculates importance per layer so compute goes where semantics live. A lightweight controller detects fine work, like grasping, and eases off to protect accuracy.
On NVIDIA A800 and RTX 3090 tests with LIBERO tasks, the method speeds inference by roughly fifty percent while holding success rates close to strong baselines. It is training free and hardware friendly, which matters for robots that live on cost bound GPUs. The diagnosis rings true, token floods and LLM backbones dominate latency, and naive pruning breaks tasks. SpecPrune VLA adds memory and structure so robots can think fast without getting clumsy, a practical win when seconds translate to mistakes on a shop floor.
6. REALBOTIX EXPANDS IN IBERIA WITH GRUPO KUO
Realbotix picked Grupo Kuo to bring its humanoids to Spain and Portugal, a partnership that blends private security with hospitality. The plan is straightforward, place approachable robots in hotels, malls, and crowded public spaces, then split their time between watchkeeping and concierge work. Grupo Kuo handles integration, service, and training. Realbotix supplies platforms tuned for lifelike motion, vision, and face to face engagement, and points to manufacturing in the United States.
Leaders frame it as a service upgrade, faster incident response for operators and friendlier wayfinding for guests. The hard part is execution. Patrols need uptime, indoor navigation that respects privacy, and clear escalation when people get involved. Around the edges, you need check in support and multilingual help that does not feel robotic. If Iberian deployments standardize playbooks for access control and customer assistance, others can reuse them without writing their own robotics curriculum. That lowers rollout friction significantly.
7. ARGENT LNG BRINGS AI AND ROBOTICS TO PORT FOURCHON

Argent LNG wants AI and robots stitched into Port Fourchon from blueprint to berth schedule. Digital twins for design reviews, computer vision for safety and quality checks, autonomous inspections in hazardous zones, and predictive maintenance once the gas starts flowing. The pitch is efficiency, lower emissions, and fewer delays at a 25 million ton export terminal that operates like an airport for ships.
Logistics is where software pays for itself. Weather windows, tug coordination, inventory balancing, and berth sequencing are perfect for optimization. Robots can take the dull and the dangerous, repeated inspections in noisy, hot areas where humans tire and miss problems. Sustainability is not a bullet point, it is a control loop that tunes process conditions in real time and produces data customers can audit. Watch partnerships, timelines, and third party verification. If the plan turns into measurable uptime and lower carbon intensity, Port Fourchon becomes a model others will copy.
8. ANT GROUP UNVEILS ROBBYANT R1 HUMANOID
Ant Group’s robotics unit, Robbyant, rolled out the R1 humanoid in Shanghai and leaned hard on software as the differentiator. The platform demonstrates balance, motion and a grab bag of service tasks from tours to pharmacy sorting. The strategy places a large model at the center, with multimodal planning for end to end chores and remote updates. Ant is training BaiLing and exploring cheaper domestic chips to keep compute costs predictable.
Early pilots focus on safety and reliability in community care and restaurants. Hardware comes from a web of suppliers, with possible work with Unitree and Orbbec. No price yet. The roadmap points to caregiver and companion roles that need long duty cycles, soft contact, and trusted reasoning. The bet is that the brain matters more than the body. If the model is strong and the platform learns fast, outsourcing parts while owning the service layer becomes a durable edge.
9. GALAXEA AI CHALLENGES TESLA WITH 700M DOLLAR HUMANOID PUSH
Galaxea AI , a Beijing startup valued near seven hundred million dollars, is scaling its R1 platform with a blunt thesis, train on the world, start with factories, then walk into homes. The current R1 is a wheeled humanoid built for precise repetitive work like parts handling. Units ship between roughly forty four and sixty four thousand dollars depending on hands and extras, with a target of one thousand deliveries by year end across China and abroad.
A biped is slated for 2026, and the team launched the G0 model in August to tighten language following and task execution. They plan to open pieces of their behavior datasets to spur progress. China is leaning in with public funding, events that normalize robots, and a supply chain that can scale. The market math grows loud, millions of humanoids over decades. If software quality holds and manufacturing ramps, R1s on factory floors become everyday sightlines.
10. NSU ROLLS OUT STARSHIP FOOD ROBOTS
Nova Southeastern University went from pilot to fleet. Seventeen Starship robots now run meals across the Fort Lauderdale campus, summoned in the Grubhub app and tracked to a chosen drop point. The pitch is predictable, fast deliveries for tight student schedules, less congestion at lines during peak hours, and a contactless option late at night. Electric drivetrains make the service quiet and light on emissions.
Safety is baked in. The cargo bay stays locked until the recipient opens it on arrival. Onboard sensors and perception keep paths clear of pedestrians and obstacles. For operations teams, the fleet adds a flexible buffer for demand spikes and a clear status view for each order. Campus leaders call it a game changer because it extends dining reach without building new storefronts. The bigger story is normalization. Delivery robots move from campus tour novelty to infrastructure that students assume will be there. Every day.
11. CIRCUS SE STARTS SHIPPING FOURTH GEN FOOD ROBOTS
Circus SE says its fourth generation CA 1 food robot rolled off a high volume line in Munich, with more units already in parallel build. The company claims automotive style quality gates, more than one hundred fifty precision checks, and a component count that rivals a small car. Partnering with Celestica signals a push from prototypes to serial manufacturing where reliability and supply chains matter as much as algorithms.
Throughput is the tell. If the line sustains thousands of units per year with stable quality, Circus clears the hardest hurdle in commercial robotics, repeatable production. The playbook continues with a second platform, CA M, aimed at defense and military kitchens that need ruggedization and uptime. Investors will watch deployment speed, error rates, and on site service data. Buyers will watch consistency, cleaning, and food safety. If both trend right, the phrase autonomous nutrition stops sounding like marketing and starts sounding like a kitchen plan. For operators.
12. FLYING CARS ROBOT DOGS AND SELF DRIVING BUSES HEADLINE MUNICH
IAA Mobility in Munich mixed car shows with near term sci fi. Xpeng paired a road car with a fold out two seat aircraft and pitched mass production in 2026. GAC’s Govy unit showed AirCab, a quiet two seater with a claimed 120 kilometers per hour top speed and orders in hand. On the ground, Unitree’s Go2 arrived in work clothes, not a lab coat, and Eve Energy’s batteries underlined China’s grip on EV supply chains.
Small autonomous shuttles, from Holon to Auve Tech, spoke to aging cities that need economical short hop transit. Xpeng’s humanoid, Iron, moved from factory training to talk of showroom roles after motion capture lessons from employees. Europe still experiments, with a leaning two wheel runabout from Wolf eMobility that already sparked a naming spat. The through line is convergence. Brands extend into air, autonomy, and embodied AI, and the category called mobility keeps expanding its borders to match new jobs for buyers.
13. HARVARD WEARABLE ROBOT RESTORES ARM MOVEMENT
Harvard engineers built a wearable robot that helps people lift and control an arm, then learns how much help to provide as the user moves. The design reads like clothing first, soft textiles, slim actuators, and sensing that stays comfortable over long sessions. As a person reaches or lifts, the controller adapts, adding assistance when muscles struggle and easing off when they can carry the load.
The aim is function for stroke survivors and people with ALS. Too much support leads to passivity. Too little makes real practice impossible. Personalization across sessions is the bridge. The group’s broader portfolio focuses on devices that are easy to don, reliable during repetitive tasks, and ready to leave the lab. What to watch are pilot studies that measure practical gains at home and in clinic, plus battery life and charging that fit real routines. Independence improves when help feels natural and always available.
14. ROBOT GUIDE DOGS SHOULD NOT BE CUTE
A Georgia Tech team asked people who are blind or partially sighted a hard question, what should a robotic guide dog look and sound like to help, not distract. The answer, approachable but not adorable. Users want signals that read as assistive tech, a vest, clear cues, quiet confidence, and no toy vibes that invite selfies. They also want voice commands that are simple and a device that docks itself to charge.
Function leads form. A robot can carry 360 degree cameras, scan for traffic and debris, understand far more spoken commands than a trained animal, and talk back with route options or warnings. It can call for help and share location if a fall is detected. The team’s point is social fit. Build for public spaces, keep noise low, and design for long wear. Adoption depends on the right mix of cues, capabilities, and restraint, not a cute mascot face.
15. CRAB BOTS TARGET SAFER LANDMINE CLEARANCE
A crab inspired program won a four year, 1.7 million dollar grant to chase a terrible ratio, mines are cheap and removal is costly. The team, led by professor Markus Nemitz, wants swarms that are cheaper to build than the threats they hunt. Designs mix soft and rigid limbs for traction across sand, rock, and tidal flats. Marine biology data guides gaits and energy use so the machines move like the animals that inspired them.
Learning handles the rest. Reinforcement loops teach robots to walk and wade across changing ground without hand tuning. Manufacturing is part of the innovation, multi material prints and robotic insertion of electronics for low unit cost and repeatability. If you can drop dozens from the air, then march them safely through danger while people hang back, clearance finally scales. The same platforms could monitor coasts, track glacier movement, or help in search and rescue where boats and trucks cannot reach.
AFTER THE HEADLINES: WHAT IT REALLY MEANS
Products Over Prototypes. The anchor theme across these Top Robotics news stories in Robotics news September 13 2025 is repeatability. Tesla’s roadmap focuses on hands, not showpieces. Circus SE talks throughput, not a sizzle reel. Nova Southeastern treats robots like campus infrastructure. When teams obsess over error rates, field service, and training playbooks, you know you are reading Robotics Advancements, not audition tapes.
Compute Moves Closer To Work. SEMICON Taiwan puts numbers behind a shift many engineers feel every day. AI is moving from rented cloud time to boards that sit inside machines. That does not kill the cloud. It expands the map. Vision models will pre filter on the edge. Heavy lifts will still run in data centers. The split helps latency sensitive tasks like manipulation, where every extra millisecond costs accuracy.
Benchmarks That Actually Matter in Robotics news September 13 2025. Berkeley’s HITTER is a small court with big lessons. Rallies past one hundred shots tell you something a single clip cannot. The robot reads spin and meets the ball with a face angle that sustains an exchange. Table tennis compresses perception, prediction, and precision into a game anyone can grade. Add lighting changes and different opponents and you get a living benchmark, not a one off stunt.
Software That Spends Compute Like Money. SpecPrune VLA is not romantic, it is practical. If a model wastes attention on repeated background and stale tokens, prune them. If the action gets delicate, ease off. This sounds like budget discipline because it is. Real robots live on cost bound GPUs. You will not always have the latest accelerator. The only way forward is code that treats cycles like cash and fights for latency without sacrificing hands.
Standards And Security Matter. SEMI’s E187 arrives with certification. That seems boring until you remember how much robotic downtime traces back to avoidable misconfigurations and weak isolation. The 3DIC alliance is the same story. When equipment builders coordinate on interfaces and test methods, integrators move faster and make fewer brittle assumptions.
New Robotics model releases Are Multiplying. Ant Group’s R1 and Galaxea’s R1 are not the same platform, yet both reflect the same play. Lean on domestically air gapped supply chains where possible, keep the brain modular, and pour capital into training data plus behavior evaluation. The winners will push software updates weekly and swap actuators only when it drops total cost of ownership. That is the lesson from phones and laptops brought into physical work.
Open Source Has A Role, Even In Humanoids, as Robotics news September 13 2025 keeps proving. You can feel an appetite for Open source Robotics projects that focus on data formats, evaluation suites, and safety checklists. Full industrial designs will remain closed for now. Shared datasets and scoring rules can still lift all boats. When teams can compare grasp stability on the same scenes, everyone learns faster. This is where universities and startups can meet on neutral ground without harming their edge.
Regulation Is Coming, So Build For It. Robotics regulation news rarely breaks the internet, yet it shapes adoption curves. If you handle food, you inherit kitchen codes. If you move indoors with cameras, you inherit privacy law. The winning teams write compliance into their build system. They log the right data, rotate keys, support audit trails, and turn yes into a one click deployment, not a frantic retrofit.
Human Factors Decide The Last Mile. The Georgia Tech guide dog work is a master class in empathy. The right design is not adorable. It is respectful, quiet, and clear about purpose. The same rule applies everywhere. Campus robots need to stop at crosswalks like a patient friend. Factory bots need handover cues that calm, not confuse. Wearables must feel like clothing, not scaffolding. You ship the social contract with the firmware.
Ports And Power Plants Are Ready For Co Pilots. Argent LNG’s plan reads like an operations manual that learned to code. Digital twins catch construction mistakes before cranes roll. Schedules move as weather shifts. Inspection routines crawl into noisy corners where people get tired fast. None of this is sci fi. It is basic math. Fewer delays, fewer accidents, and better documentation make a terminal cheaper to run and easier to insure.
Why This Edition Matters. The phrase Robotics news September 13 2025 signals a timeline, yet the deeper pattern is compounding capability. Hardware improves by inches. Software improves by updates. Integration improves by checklists. Together they move the frontier from a lab to the rest of the map. If you track Robotics and tech developments past 24 hours, you can miss the signal in the noise. The signal is system thinking, not a single shiny clip.
A Quick Playbook For Builders, drawn from Robotics news September 13 2025
• Pick a benchmark with a scoreboard. Rally length. Pick rate. Mean time between failures.
• Spend compute like cash. Profile, prune, and cache.
• Treat safety as a feature, not a checkbox.
• Start with one boring workflow and make it sing.
Where The Next Sparks May Fly. Watch Boston Dynamics update its manipulation stacks and the choreography that keeps legs balanced during reach. Watch Tesla news for real factory placements of Optimus hands, not stage cameos. Watch whether campus fleets federate into city networks that share maps and curb data. Watch for New Robotics papers arXiv that turn benchmarks into leaderboards. Then ask how to ship the gain from a poster to a plan.
Context For Readers. This is Robotics news September 13 2025 with a purpose, cut through noise and deliver a map you can use. It is also a ledger of Artificial intelligence breakthroughs. Each item ties to a real workflow, often one you would not notice unless it failed. That is why this beat keeps getting better. The work gets measured, then it gets shipped, then it gets boring in the best way.
CONCLUSION AND CALL TO ACTION
If you made it here, you already know the pattern. The best Robotics News is not viral, it is reliable. This week’s set shows how fast that reliability is scaling. Hands learn to grip. Schedules learn to move. Wearables learn to help without getting in the way. The result is simple. Better work, less waste, and more time for the parts only people can do.
I will keep tracking Robotics news September 13 2025 quality signals, not hype, and I want your eyes on the ground. If you deploy a fleet, wire a factory cell, or test a new benchmark, tell me what really worked. Subscribe, share with a friend who builds, and send me the toughest workflow that still feels stuck. Next week we will bring the same lens to a fresh set of headlines, again under the banner of Robotics news September 13 2025, and we will turn noise into plans.
1) What are the top stories in Robotics news September 13 2025?
A strong week for real deployments and chip ecosystem moves. SEMICON Taiwan highlighted a new 3DIC alliance and certification for the E187 cybersecurity standard, signaling how fast AI hardware and packaging are consolidating.
2) Did a humanoid really rally 100+ shots at the ping-pong table?
Yes. UC Berkeley’s HITTER system achieved up to 106 consecutive shots against a human, using a hierarchical planner plus RL whole-body control, a standout demo repeatedly cited in Robotics news September 13 2025.
3) Which new research papers should I read from Robotics news September 13 2025?
Start with SpecPrune-VLA, a training-free method that speeds VLA inference about 1.5× on A800 and RTX 3090 with minimal success loss. Pair it with SLiG-Net, which couples low-light enhancement with grasp pose planning for space robotics.
4) What actually shipped or scaled in the real world in Robotics news September 13 2025?
NSU expanded its Starship food-delivery fleet to 17 robots, Circus SE began delivering fourth-gen CA-1 kitchen robots from a new high-volume factory, Realbotix signed an Iberian distribution deal, and Argent LNG outlined an AI plus robotics plan for Port Fourchon.
5) Who entered or advanced in the humanoid race highlighted in Robotics news September 13 2025?
Ant Group unveiled its Robbyant R1 humanoid at IFA and the Inclusion Conference, while Beijing’s Galaxea AI hit a 700 million dollar valuation as it scales R1 deployments. Both underscore China’s accelerating push alongside US players.